





Amazing phenomena and unbelievable facts in electromagnetism and wave physics
Due to access restrictions, alternative internal and external links are provided for each content.
Wave-particle duality paradox - The century-old mystery in physics
Light exhibits dual behavior, showing both wave-like and particle-like properties depending on experimental conditions. This amazing phenomenon, known as "wave-particle duality," is one of the most fundamental concepts in quantum mechanics.
In quantum mechanics, this duality is explained by the concept of wave function. Photons remain in a "superposition" state until measured, and when measured, they exhibit either particle or wave behavior.
Conclusion: Light is neither completely a wave nor completely a particle, but rather a quantum entity that exhibits these properties depending on conditions. This deeper understanding of light's nature opens the door to better comprehension of the quantum world.
The search for separate magnetic charges - An unsolved mystery of modern physics
The magnetic monopole is one of the most fascinating and mysterious concepts in modern physics. While we can easily have separate positive and negative electric charges, we have never been able to observe a completely separate north or south magnetic pole in nature.
In quantum field theory, magnetic monopoles are considered as "topological solitons". These theoretical entities have very large masses (around 10^16 GeV) and therefore their production in current accelerators is impossible.
Conclusion: Although no magnetic monopole has been experimentally observed so far, the search for them continues. The discovery of such a particle would not only bring the Nobel Prize to its discoverers but would also transform our understanding of the fundamental laws of the universe.
Cosmic speed limit - Boundaries of relativistic physics
According to Einstein's special theory of relativity, the speed of light in vacuum (approximately 300,000 km/s) acts as an ultimate limit in the universe. This speed is not only a ceiling for light but also for any type of information or particle.
In quantum mechanics, concepts like "delayed choice quantum" and "Casimir effect" have been proposed that are sometimes mistakenly interpreted as violations of light speed. But in all these cases, no information or matter is transmitted faster than light.
Conclusion: So far, no experimental evidence has been observed for faster-than-light motion in vacuum. All experiments and astronomical observations confirm that the speed of light is a fundamental constant in the universe.
Quantum fluctuations and virtual particles - A hidden world within nothingness
Contrary to the classical conception of vacuum as "absolute nothingness," quantum physics shows that vacuum is actually a very dynamic and active environment. According to quantum field theory, vacuum is filled with permanent activities and energy fluctuations that govern the universe at the smallest scales.
In quantum field theory, vacuum is defined as the "ground state" of the system - a state with the lowest possible energy, but not zero energy. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle doesn't allow energy to be exactly zero, so quantum fluctuations always exist.
Conclusion: Quantum vacuum is by no means "empty," but rather a dynamic environment full of activity that determines the fundamental properties of matter and forces. This new understanding of vacuum is one of the deepest insights of modern physics.
Rayleigh scattering - The secret of the daily rainbow
The phenomenon of the blue sky is one of the most beautiful and yet most scientific displays of nature, explained by a physical phenomenon called "Rayleigh scattering." This phenomenon describes how sunlight interacts with molecules in Earth's atmosphere.
From a microscopic viewpoint, Rayleigh scattering results from "interaction of photons with electrons of air molecules". When a photon interacts with an electron, it excites the electron to a higher state, and then the photon is emitted with the same energy but in a different direction.
Conclusion: The blueness of Earth's sky is a direct result of atmospheric composition, air molecule size, and physical properties of light. This phenomenon is not only beautiful but also evidence of our deep understanding of light physics and its interaction with matter.
Metamaterials and optics - Technological frontiers in light engineering
The idea of invisibility has always been at the boundary between science and imagination. Although complete and all-around invisibility remains a major challenge, recent advances in metamaterial technology and transformation optics have opened new ways to manipulate light and create limited invisibility effects.
Metamaterials use "resonant structures" at the nanoscale to create unusual electromagnetic properties. These materials can guide light in such a way that it appears as if no object is in its path, with precise control of phase and speed of light around the object.
Conclusion: Although complete invisibility of humans or large objects is still in the distant future, significant progress has been made in this field. Current technologies are more like "light deflection" than "true invisibility," but the path for future research has been paved.
Fundamental understanding of electromagnetic waves
We are floating in a sea of electromagnetic waves. Our universe is filled with these waves, from radio waves that play music to visible light that allows us to see the world and gamma rays that come from the depths of space.
Sunlight is a traveler from the past. When sunlight touches your skin, you are actually receiving rays that separated from the sun about 8 minutes and 20 seconds ago. At every moment, you are seeing the "image" of the sun's past.
Your microwave and mobile phone are from the same family. Microwave waves used for heating food and also for communication by mobile phones and Wi-Fi are all electromagnetic waves.
Converter of electrical energy to electromagnetic waves
Antennas are amazing converters that transform electrical energy into electromagnetic waves (and vice versa). When electric current passes through an antenna, electric and magnetic fields are created around it, and these fields separate from the antenna and propagate through space as radio waves.
Antenna operation is based on the principle of resonance. Each antenna is optimized for a specific frequency range. When electromagnetic waves with appropriate frequency hit the antenna, they create "resonance" in the antenna and produce a weak electric current that is then amplified and processed by the receiving device.
A tremendous transformation in wireless communications
Smart antennas, also known as adaptive antennas or MIMO antenna array systems, are an advanced generation of antenna technology that, by utilizing digital signal processing, dramatically transforms the performance of wireless networks.
Unlike conventional antennas that radiate signals uniformly in all directions, smart antennas consist of multiple radiating elements. This system, by analyzing incoming signals from different users in real-time, has the capability of beamforming and spatial tracking.
Understanding the dual nature of light
Light is one of the most fundamental and yet mysterious phenomena in the universe. Scientists have been trying to understand the true nature of light for centuries, and the answer to the question "What is light really?" constitutes one of the most amazing stories in the science of physics.
According to quantum theory, light exhibits dual behavior. Sometimes it behaves like a wave that propagates through space and creates phenomena such as interference and diffraction, and sometimes it acts like a particle (photon) that carries discrete energy.
Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
Laser, which stands for "Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation", is considered one of the most amazing inventions of the 20th century. Unlike ordinary light that scatters in all directions, laser light is completely monochromatic, coherent and directional, and these characteristics have made it an extremely precise tool.
The basis of laser operation is based on the phenomenon of "stimulated emission". In this phenomenon, excited atoms, with the passage of photons, emit completely similar photons, and this process leads to light amplification and production of laser beam.
The four equations that built the modern world
Interactive display of how magnetic fields are created by varying electric fields and vice versa
Discover how Maxwell's equations describe the fundamental behavior of electromagnetic fields.
Interactive tool for displaying different antenna radiation patterns and gain

Simulate how different antenna designs radiate energy in three-dimensional space.
Display of constructive and destructive interference of electromagnetic waves
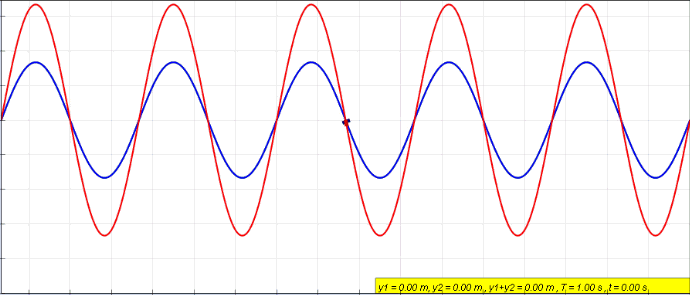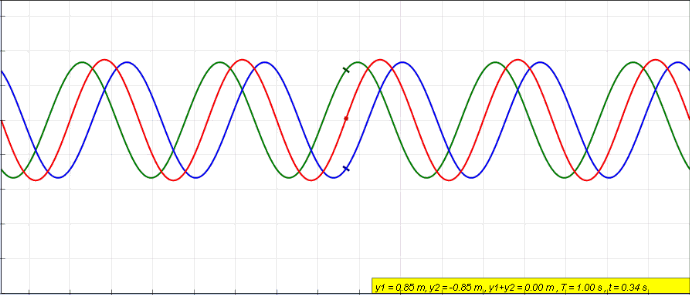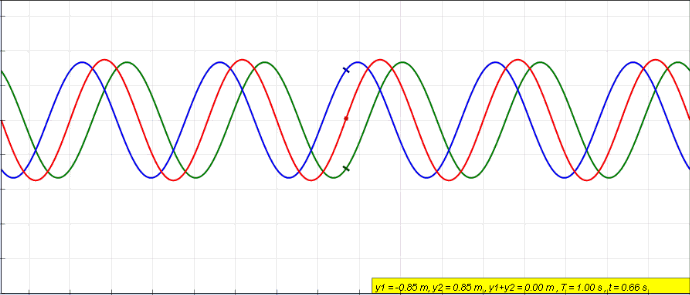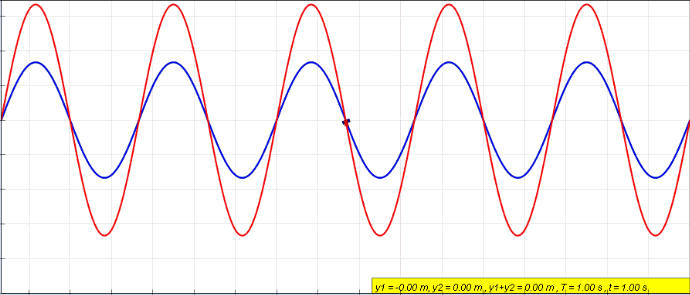
Experiment with wave sources and observe interference patterns.
Analysis of electric and magnetic fields in circuits and space
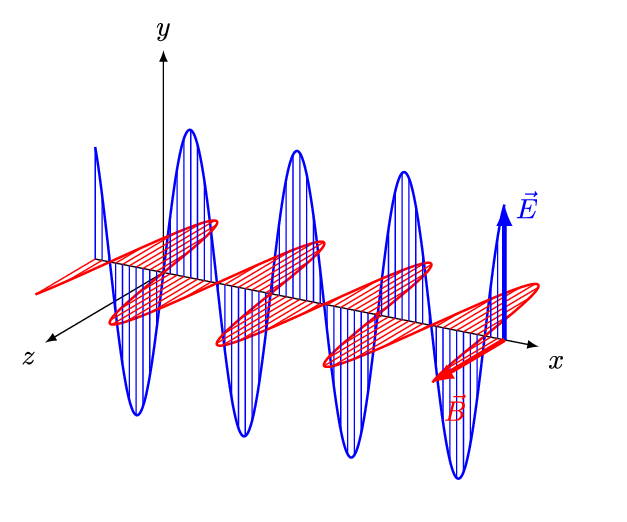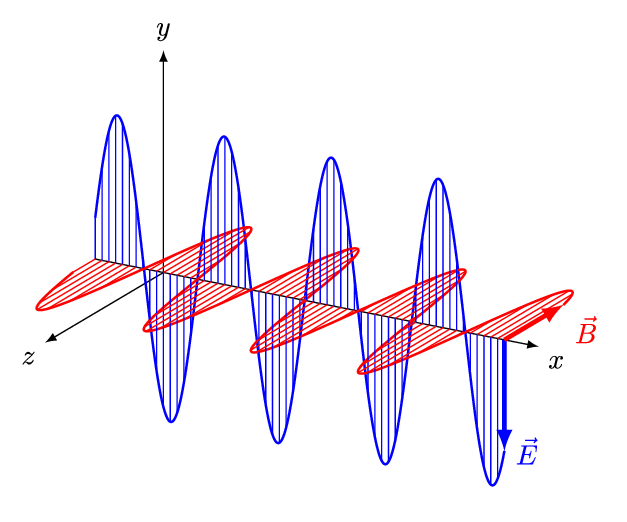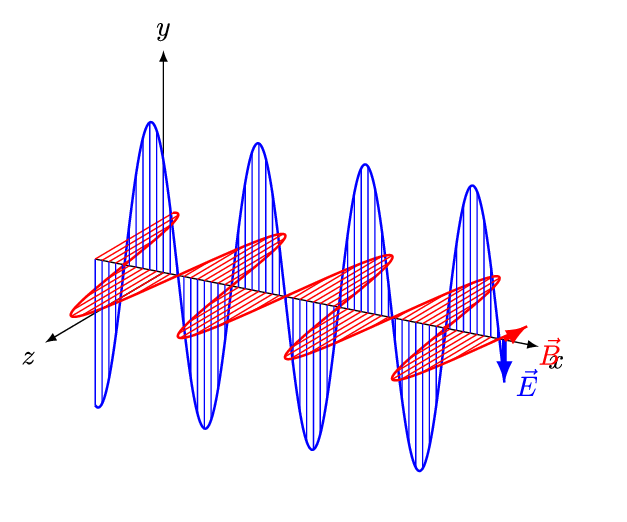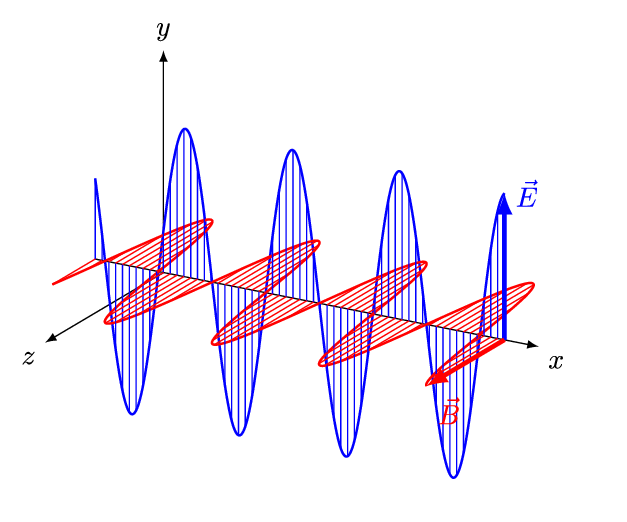
Examine the behavior of electromagnetic fields at different frequencies.
Lightning can produce positrons (electron antimatter) through photonuclear reactions
GPS satellites must account for both special and general relativity effects to maintain accuracy
Under special conditions, humans can "see" radio waves as flashes of light when they pass through the visual cortex
You can download files and simulations
Educational videos are accessible on different platforms
Educational materials are provided as PDF